Corrosion control for the pulp and paper industry
Increase operational reliability
Creating paper out of wood or pulp involves several complex processing steps in which the raw materials are chemically treated. This produces gases that have the potential to cause corrosive damage to the surrounding machinery and equipment. That is why they are classed as contaminant gases.
Pollutant gases in the pulp and paper industry
| Pollutant gases | Process | Viledon ChemControl pellets |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) | Lignin removal (sulfite process) wastewater treatment | CCP 104, CCP 108, CCP 210, CCP 310, CCP 810 |
| Mercaptans | Lignin removal (sulfite process) | CCP 104, CCP 108, CCP 210 |
| Sulfur dioxide (SO₂) | Lignin removal (sulfite process) | CCP 104, CCP 108, CCP 210, CCP 310, CCP 810 |
| Sulfur oxide | Bleaching of waste paper, bleaching of wood pulp | CCP 104, CCP 108, CCP 210, CCP 310 |
| Chlorine (Cl₂) | Bleaching of pulp | CCP 310, CCP 510, CCP 610 |
| Chlorine oxide (ClOₓ) | Bleaching of pulp | CCP 310, CCP 510, CCP 610 |
| Ozone (O₃) | Bleaching of pulp | CCP 310, CCP 610 |
Key process steps in papermaking
Particularly at risk are sensitive areas such as electronic equipment, control rooms, process control systems and compressors. The negative effects of the corrosion of the copper and silver components of these devices include a loss of process efficiency, additional maintenance costs, expensive repairs and unplanned downtime.
We provide reliable protection against corrosion by contaminant gases that are released during the main process steps in papermaking.

Lignin removal
You remove lignin from the raw materials. We remove contaminant gases from the air.
The technical removal of lignin is a key processing step during the manufacture of pulp. In chemical processes, the lignin needs to be dissolved from the lignocellulose and subsequently removed from the production process. Two methods have been established and are particularly important in pulp production: the sulphate and sulphite processes (see below). Depending on the procedure, various contaminant gases are released. Using different filtration media, we remove these from the air and prevent the corrosion of sensitive equipment.

Bleaching
Bleaching protects paper against yellowing. Gas phase filtration protects equipment against corrosion.
Whether using wood pulp, pulp or waste paper: bleaching is an essential process step in paper production to remove unwanted stains. Because lignin is responsible for the yellowing of paper, it needs to be removed during the bleaching process. This ensures that the paper stays white. Bleaching is achieved via a technical process involving mainly chlorine bleach or a bleach with oxygen, chlorine dioxide, hydrogen peroxide or ozone. Depending on the chemical substances involved, this leads to the creation of various contaminant gases that need to be removed from the air.

Wastewater treatment
You ensure clean water. We ensure clean air.
At the end of the papermaking process comes the treatment of wastewater. This involves removing the polluting elements from the wastewater to restore its natural quality.
On the way from the dischargers to the sewage treatment plant, water purification is achieved through targeted chemical additives and biological processes. In the anaerobic environment, contaminant gases such as hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) are created.
This gas has the characteristic pungent odor of rotten eggs. Even more problematic than the smell, however, are the effects it has on humans and sensitive electronic components. Using special pellets and individual filtration concepts, we reliably remove hydrogen sulfide from the air.


Viledon filterCair modules
Customized service package for your needs
With the Viledon filterCair modules, we offer you a comprehensive range of problem-specific services that can also be individually combined.
Benefit from our specialized expertise in gas phase filtration.
Select and request detailed information.
Discover our products for gas phase filtration.
Click on details for more information. Technical data and specific product features can be found in the e-catalog.
Comprehensive pellets portfolio for the reliable removal of contaminant gases by means of adsorption, absorption and chemisorption. Depending on the process requirement different pellets are used.
The future of air purification technology: The special structure of the media allows a highly efficient interaction between the carbon and the air. Adaptable to specific performance requirements on site.
Rugged plastic housings that contain ChemControl Pellets for chemical filtration. Available in four sizes to equip systems for almost all applications. Easy handling and replacement.
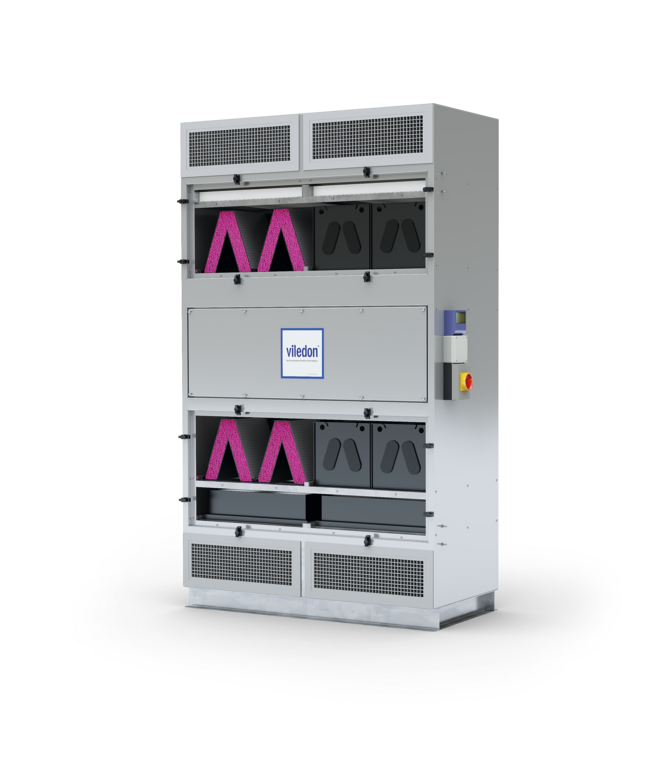
Multi-stage filtration systems with ChemControl pellets for the efficient and safe removal of contaminant gases. A pre- and fine filtration also ensures optimum protection against particles.
Multi-stage filtration systems with Honeycomb (HM) modules mounted on skids. Provide highly purified makeup air for pressurizing control rooms to prevent the intrusion of contaminated air.
A maximum application flexibility with easy handling and highest cost-effectiveness. Filled with different Viledon ChemControl pellets depending on the process requirements.
Measures and monitors the corrosivity of air in rooms via copper and silver sensors. The only online monitoring system with a large color display for clear visibility at a glance.